 I originally wrote this way back in 2012 and it is a popular article, with around 45,000 views. It was due a major update, so here it is.
I originally wrote this way back in 2012 and it is a popular article, with around 45,000 views. It was due a major update, so here it is.
A lot of drivers get confused by roundabouts, and I’m not just talking about learners. Signalling, lane choice, and lane discipline seem to provide huge challenges for many people.
The Highway Code (HC) says this about roundabouts:
Rule 185
When reaching the roundabout you should
- give priority to traffic approaching from your right, unless directed otherwise by signs, road markings or traffic lights
- check whether road markings allow you to enter the roundabout without giving way. If so, proceed, but still look to the right before joining
- watch out for all other road users already on the roundabout; be aware they may not be signalling correctly or at all
- look forward before moving off to make sure traffic in front has moved off.Rule 186Signals and position.When taking the first exit to the left, unless signs or markings indicate otherwise
- signal left and approach in the left-hand lane
- keep to the left on the roundabout and continue signalling left to leaveWhen taking an exit to the right or going full circle, unless signs or markings indicate otherwise
- signal right and approach in the right-hand lane
- keep to the right on the roundabout until you need to change lanes to exit the roundabout
- signal left after you have passed the exit before the one you wantWhen taking any intermediate exit, unless signs or markings indicate otherwise
- select the appropriate lane on approach to the roundabout
- you should not normally need to signal on approach
- stay in this lane until you need to alter course to exit the roundabout
- signal left after you have passed the exit before the one you wantWhen there are more than three lanes at the entrance to a roundabout, use the most appropriate lane on approach and through it.
This is very straightforward. However, you have big roundabouts, small ones, ones with only one lane, and others with multiple lanes. Some junctions consist of two or more roundabouts in quick succession, and then you can have complex junctions with flyovers, and roundabouts underneath them. A lot of drivers have problems even with the simple ones, and the more complex ones can be hotspots for minor bumps or worse.
The bottom line, though, is that although every junction is different and there is no single ‘golden rule’ which governs how you negotiate them, almost every individual roundabout works according to what the HC says in Rules 185 and 186.
Unmarked Roundabouts
 The simplest type of roundabout is unmarked, single lane, usually quite small, and pretty much symmetrical as far as the feed roads are concerned.
The simplest type of roundabout is unmarked, single lane, usually quite small, and pretty much symmetrical as far as the feed roads are concerned.
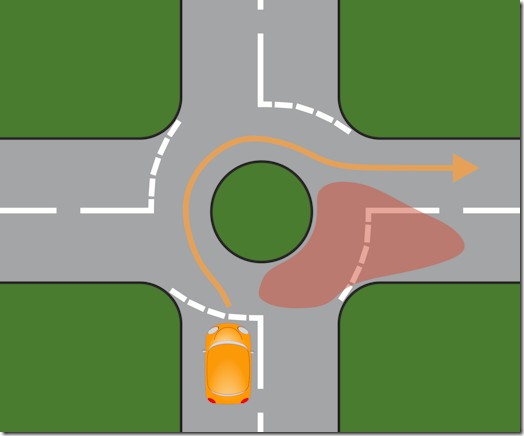
When the HC talks of ‘exits’, the standard system is that the road you are approaching on isn’t numbered, so in this diagram a left turn is the 1st exit, straight on is the 2nd exit, and right is the 3rd exit, Only if you are using the roundabout to go back the way you came does the road you are approaching on become the 4th exit.
Road signs with roundabout directions like this one always assume you are approaching from the bottom.
As you approach it, you should signal left if you’re taking the 1st exit, and right if you’re taking the 3rd or 4th exits. You do not signal for the straight ahead (2nd) exit as you approach the roundabout.
When you reach the roundabout, and once it is safe to proceed on to it, you steer a path around it and signal left at the exit immediately before the one you intend to leave by. Your position as you drive around the roundabout is not really important if it is only wide enough for one car.
If the roundabout is wide enough to accommodate two cars side by side as they pass round it, then you should adopt the left-hand lane position if you’re taking the 1st or 2nd exits in this example. You would adopt the right-hand position if you’re taking the 3rd or 4th exits. Remember that as you take the exit you require, if you are in the right-hand lane position you will need to have a quick glance in your mirrors to make sure no one is trying to overtake on your left. If you don’t follow this lane discipline on a wider roundabout, people could potentially be trying to get past on either side as you exit.
Lane discipline is the biggest factor in people’s inability to deal with roundabouts. It’s also one of the most common reasons for failing driving tests. In most cases, people are not even aware that there are ‘lanes’ they should be following. This can be more of an issue with unmarked roundabouts, where the ‘lanes’ need to be visualised even though there are no white lines telling you where they are.
Not adhering to lane positions on roundabouts is called ‘straight lining’. It isn’t illegal, but it is an advanced driving technique which requires planning and good all-round awareness. When learners and new drivers do it, they are not applying any advanced driving skills – they’re just weaving all over the road without realising it.
 Of course, most roundabouts are not perfectly symmetrical – and this is where many driving instructors try to simplify things by making them a hundred times more complicated using silly rules. Let’s get one of them out of the way immediately: there is no such thing as ‘the 12 o’clock rule’.
Of course, most roundabouts are not perfectly symmetrical – and this is where many driving instructors try to simplify things by making them a hundred times more complicated using silly rules. Let’s get one of them out of the way immediately: there is no such thing as ‘the 12 o’clock rule’.
At some point in the distant past, someone somewhere tried to create an all-encompassing rule that worked for all roundabouts. They came up with ‘the 12 o’clock rule’, and so ingrained did it become that even BSM used to teach it as gospel at one time (it may have been BSM who invented it). But there is a problem with it – it doesn’t work all the time, so it cannot possibly be called ‘a rule’. In some situations, it inconveniences others and is actually dangerous.
You can see that this roundabout layout is identical to the first one, other than the 2nd exit is slightly further round. The ‘12 o’clock rule’ divides the roundabout into a clock face, and argues that any exit after the 12 o’clock position is a right turn! This is nonsense in the majority of cases, and the last thing a new and nervous driver who is already struggling with roundabouts needs is to have to decide whether the road they want is after 12 o’clock or not on top of everything else. Many such roundabouts won’t have a sign in the first place to help decide, and even the ones that do may have a symmetrical one like the first example, when the actual road layout is more like the second. And then there is the physical appearance of the road layout as you approach it at ground level – the approach roads may well have bends on them which give the illusion of an exit being in one location on the clock face when it is actually elsewhere.
If you indicate right approaching such a roundabout, at least some – probably the majority – of the people around you will assume you are taking the 3rd or 4th exit – actually turning right. If they then tried to zip past you to take the 2nd exit – irrespective of any argument that they shouldn’t assume anything – you suddenly cutting across to take it as well is not going to end happily. This is even more likely if your other problems means your lane discipline or late signalling is conveying the wrong message as well.
Not all roundabouts are limited to just four exits – they can have anywhere from two and upwards, though they’re more likely to be marked roundabouts the more exits they have.
In general, your lane positioning and signalling on approach to an unmarked asymmetrical roundabout should be exactly the same as for the symmetrical ones. However, there are some instances where treating a 2nd exit that is a long way round as a right turn would make sense. Like this one.
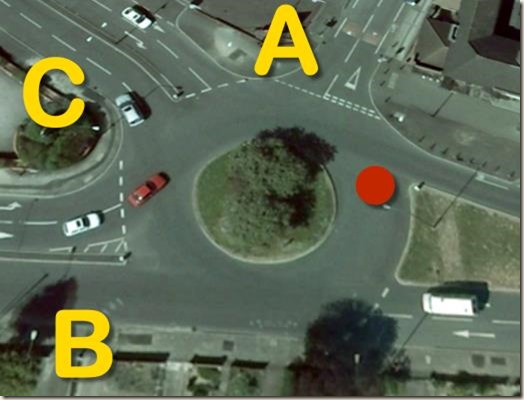 This used to be on every test candidate’s test when there was a test centre at Chalfont Drive in Nottingham, and as they drove off at the start of their test they immediately came to the point ‘A’. I still take people to it now so I can show them different roundabouts and how they work.
This used to be on every test candidate’s test when there was a test centre at Chalfont Drive in Nottingham, and as they drove off at the start of their test they immediately came to the point ‘A’. I still take people to it now so I can show them different roundabouts and how they work.
My advice to my pupils when they reach this one is to indicate right if they’re taking the 2nd (B) or 3rd (C) exits. The 2nd exit is so far round it makes sense to do so, and it also tells drivers coming in from the unmarked road at the bottom right of this picture that they intend to pass in front of them and haven’t just forgotten to signal. If my pupil is taking the 2nd exit (B), they signal left at the red dot. If they’re taking the 3rd exit, they signal left as they pass B.
It is worth noting that if a candidate didn’t signal right here, as long as they signalled left in good time to take the 2nd exit without confusing drivers waiting at C then they would not have been faulted for it. Likewise, if they signalled right and left it late to signal left, perhaps causing those waiting at C to pause, then they easily could have been (which is true on any roundabout). The way I teach it is intended to get them to think about things, and not to blindly apply silly rules which achieve nothing.
Basically, if the 2nd exit is very much further to the right, a signal might make sense. But it is not because of ‘the 12 o’clock rule’. Your choice of a signal and lane position is not automatic, and depends on the individual roundabout and the circumstances at the time.
Here are some more examples of unmarked roundabouts. As I said earlier, all roundabouts are different, though the basic principle you use on them is given in the HC. These examples are all in Nottingham. Some are on test routes, and some aren’t. Some of them don’t exist anymore (thanks to Nottingham’s tram).
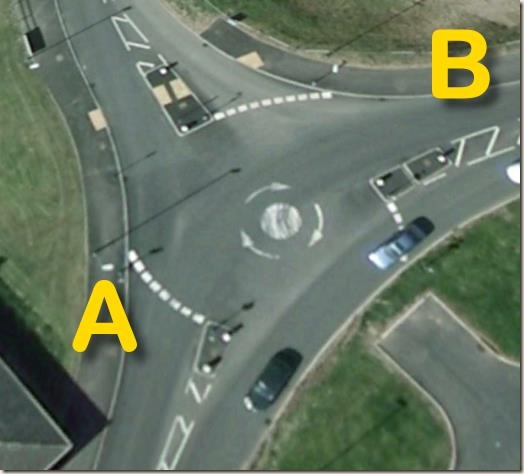 This one is a mini-roundabout in West Bridgford. The majority of traffic passes A-B and B-A (the side road has busier periods as it leads to a sports ground and school).
This one is a mini-roundabout in West Bridgford. The majority of traffic passes A-B and B-A (the side road has busier periods as it leads to a sports ground and school).
Travelling A-B, no signal is needed (even if B is past 12 o’clock). If you signalled right, people travelling B-A would have to assume you were turning around and were going to pass in front of them, so they’d stop. And I can assure you that it is annoying when someone signals needlessly, especially because sometimes people are turning around and it gets confusing.
Travelling B-A, a left signal is a positive indication to those travelling A-B that you are not intending to turn in front of them into the school or sports ground. This principle applies to most three-exit roundabouts where there are no marked lanes. However, if you didn’t signal on your test in such a situation it probably wouldn’t be marked.
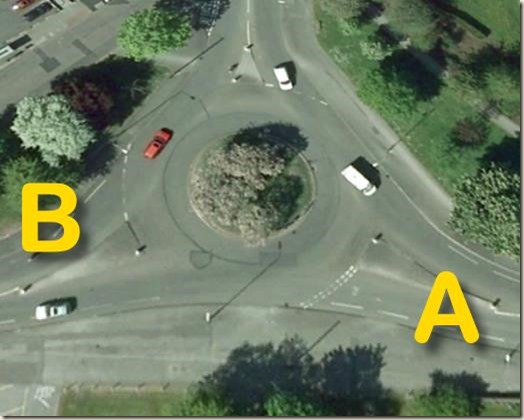 This one doesn’t exist anymore. It was a three-exit roundabout. If you were travelling A-B (which is literally following the road ahead), a left signal told those at B that you weren’t turning in front of them. Travelling B-A would not have required a signal – although in this case, if you had signalled it would have been less of an issue because of the size of the whole layout. But it was still totally unnecessary, and if you had delayed giving a left signal to exit but were still signalling right, that could have been seen as a fault – especially if someone was waiting at A.
This one doesn’t exist anymore. It was a three-exit roundabout. If you were travelling A-B (which is literally following the road ahead), a left signal told those at B that you weren’t turning in front of them. Travelling B-A would not have required a signal – although in this case, if you had signalled it would have been less of an issue because of the size of the whole layout. But it was still totally unnecessary, and if you had delayed giving a left signal to exit but were still signalling right, that could have been seen as a fault – especially if someone was waiting at A.
I must repeat again that every roundabout is slightly different and sometimes only experience can teach the best way of dealing with them. There is also the issue of other people not signalling at all, or signalling incorrectly, so it’s best if you don’t add to it by joining them. If a signal isn’t specifically (and correctly) telling someone something they need to know precisely when they need to know it, then it is more than likely going to add even more confusion to a situation.
Think about what you are doing, and don’t try to blindly follow artificial rules that are intended to achieve think for you.
Marked Roundabouts
Larger roundabouts, like the one shown at the start of this article, usually have road markings to define lanes and show routes. They often have multiple intermediate exits of differing sizes and priorities, and you’ll sometimes see them described as gyratory or spiral roundabouts. These are the ones that people seem to fret about the most, but they are actually very easy to deal with once you know what you’re doing. Personally, I don’t like the terms ‘gyratory’ or ‘spiral’ because technically these apply to all roundabouts. The markings just guide you, and making a big deal out of them by giving them special names just scares (and confuses) pupils even more.
I’ve written a separate article about the Nuthall roundabout, partly as an illustration of how ‘the 12 o’clock rule’ doesn’t work reliably. This roundabout is huge and the island itself is raised and covered in trees, which means the intermediate exits are not visible. You have to look for and use the road markings and road signs to plan your way through. In all honesty, anyone encountering it for the first time probably wouldn’t stand a chance of doing it properly, especially a learner. And since there’s a high probability of having to drive on it if you have your test at the Watnall Test Centre, pupils need to be able to handle it.
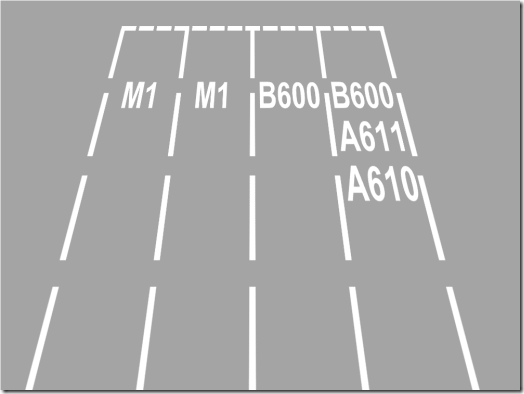 This diagram above shows how the road markings appear as you approach the roundabout along the A6002 Woodhouse Way heading towards the city centre (any large roundabout in any other city would have similar markings). The A6002 is a single lane road, but on approach to the roundabout it widens dramatically and splits into four lanes. It is important to know where you are going and to get into the correct lane straight away – or rather, not to leave it too late to get into the correct lane. For example, if you know you want to exit along the A610 towards Nottingham, then you should ideally go straight into the right hand lane which has the A610 route marked in it. Failing that, you will need to move safely into that lane once you see the road markings – though on your test this is a much more risky strategy because there will likely be other traffic already moving in behind you.
This diagram above shows how the road markings appear as you approach the roundabout along the A6002 Woodhouse Way heading towards the city centre (any large roundabout in any other city would have similar markings). The A6002 is a single lane road, but on approach to the roundabout it widens dramatically and splits into four lanes. It is important to know where you are going and to get into the correct lane straight away – or rather, not to leave it too late to get into the correct lane. For example, if you know you want to exit along the A610 towards Nottingham, then you should ideally go straight into the right hand lane which has the A610 route marked in it. Failing that, you will need to move safely into that lane once you see the road markings – though on your test this is a much more risky strategy because there will likely be other traffic already moving in behind you.
Absolutely the worst thing you can do is leave it too late and end up in one of the other lanes, and then try to get over at the last minute – by then, other traffic will have boxed you in. The option of switching lanes on the roundabout itself is only marginally better, and relies on extremely good observation and a lot of luck. Of course, many drivers out there do it wrong all the time, but they aren’t on their tests and they simply end up annoying other drivers and putting dents in their cars as a result.
As I said, the Nuthall roundabout would be very difficult for anyone to do correctly if they hadn’t done it before, let alone a learner meeting it for the first time on their test. So a good driving instructor will make sure their pupil knows how to negotiate this sort of roundabout before they go to test. That applies everywhere – not just in Nottingham – because these sorts of road systems exist all over the country. And a good learner will learn to understand what is happening so they can deal with it and apply it when they start driving by themselves.
Once you’re in the correct approach lane it is then vital to stay in that lane and make the valid choice of available lanes in front of you as you enter the roundabout. The approach lane for the A610 here can then branch off towards B600 or A611, and you have to make the correct choice.
The main reason learners have such problems staying in lane (referred to as ‘lane discipline’ when it is marked on test by an examiner) is down to the fact they don’t even see (or aren’t aware of) lanes or lane markings as they’re driving along. 
If you look at the diagram above you can see a single lane represented as though you were looking at it out of the front of the car. You can visualise it in various ways, and one method is imagine that the white lines form the rails that a train is running along. The driver has to stay between them.
Unlike a train, which is more or less fixed to the rails, a car driver has to keep between the rails by steering – and they can only do that if they are looking at the rails, seeing them, and being aware of them all the time. That’s where it breaks down with many learners, and when I discuss it with mine one of the most common comments is that they get confused by ‘all those lines crossing’.

In this diagram, you have the same layout as above, but with the added complication of other sets of rails crisscrossing it. The trick is to only look at your set of rails – the others are nothing to do with where you want to go.
You seldom need to make sharp turns on a roundabout, and your route will be a smooth and gentle series of curves (or rails). Switching to one of those other sets of rails would not be smooth.
Being stressed affects how easily drivers see these lines. One of the things I do with my pupils involves ‘scaling’. I ask them to imagine that they’re sitting at home with their feet up, just after a meal, a nice drink in their hand near a warm fire watching TV – that’s 0 on the scale. Then I ask them, for example, to imagine having just jumped out of an aeroplane on their first ever parachute jump, knowing that someone they had an argument with last night had packed their parachute – that’s 100 on the scale. Then I ask them what number on that same 0-100 scale (which I call their stress-o-meter) they are imagining in various situations when we’re on lessons. This can be a real eye-opener. Some of them will surprise you and tell you they’re over 80 even when driving normally on a clear road. However, whatever their ‘normal’ number, if it goes up near a roundabout this will tell you they’re effectively ‘going blind’ when they try to negotiate it. And I am certain that a lot of ‘experienced’ drivers have the same problem every day of their lives.
Stress acts like a veil or blindfold. Everyone has a different threshold, but at some point an individual’s stress level starts to prevent them from thinking or seeing clearly. Things go out of focus or even disappear completely.
Are roundabouts classed as junctions?
Yes. Any point where two or more roads meet or cross is a junction, so roundabouts are also junctions, but they have their own rules compared to T-junctions and crossroads.
What are the signalling rules at roundabouts?
Read HC Rule 186. You normally signal left or right on approach only for the first or last exits (or full circle). Intermediate exits normally don’t need an approach signal. When leaving the roundabout every exit is a left turn, so you normally indicate left at the exit just before the one you want.What is the Highway Code 12 o’clock rule?
There isn’t one! This is a fabricated ‘rule’ which doesn’t work, and leads to confusion for you and other road users when used blindly. The HC says that on approach you shouldn’t normally need to indicate for any intermediate exit.
There are some roundabouts where the intermediate exit you want is so far to the right that a signal might well benefit other drivers, but there are far more situations where it would definitely confuse them.
Doesn’t the Highway Code wording automatically imply the 12 o’clock rule?
Not in the slightest. I saw someone on social media make that claim and couldn’t believe my eyes. They actually stated that it is in the HC. If anything, the HC explicitly refutes the ‘12 o’clock rule’. It is not in the HC.
But the 12 o’clock rule is just a way to help learners when they’re starting out.
There are other users on the road. You do realise that, don’t you? If I’m waiting to emerge on to a busy roundabout and see someone coming round it with their right indicator on, I will wait – and it is bloody annoying when they then exit left before they get to me. So I end up waiting for longer. That’s what happens when you indicate right unnecessarily when you’re going ahead at a roundabout. You confuse other people because you’re giving the wrong signals.
Learners should understand what they are doing, not just following stupid rules made up by people who understand little more than their pupils do. The ‘12 o’clock rule’ does not work.
How do you teach roundabouts not using the 12 o’clock rule?
This is where an ADI earns their money. In most cases, the reason pupils can’t do roundabouts is because they panic and everything becomes a blur – they’re worried about all the other traffic on the roundabout and, as a result, lose sight of the lanes. They need to be able to bring things back into focus and learn how to deal with what is, after all, only a simple junction. What I normally do is sketch a diagram of a crossroads, and tell them I want them to turn right, so who do they have to look out for before they go? We start with something like this.
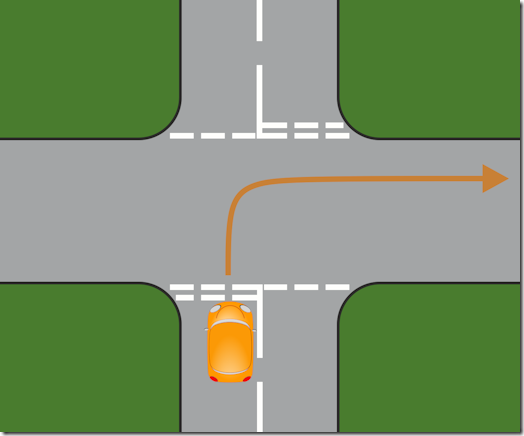 I ask them to imagine they’re in the yellow car and they want to turn right – where do they need to check before they go? After a while, we’ll have touched all the bases – cars from the left turning to their left, right into our road, or going ahead; then the same for cars from the right, and cars in front of us. We end up with something like this.
I ask them to imagine they’re in the yellow car and they want to turn right – where do they need to check before they go? After a while, we’ll have touched all the bases – cars from the left turning to their left, right into our road, or going ahead; then the same for cars from the right, and cars in front of us. We end up with something like this.
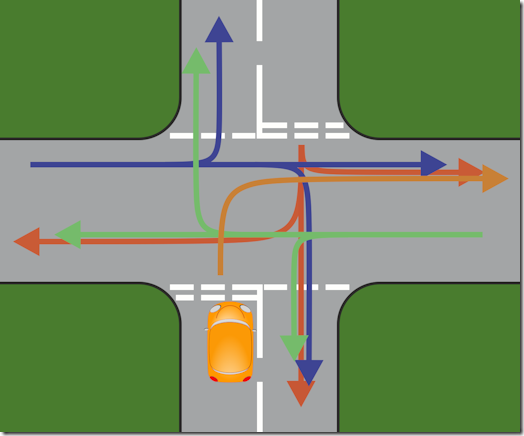 I point out to them that they can handle all that without any issue (well, most of them), even though all the possibilities of where traffic is coming from are quite complicated to assess.
I point out to them that they can handle all that without any issue (well, most of them), even though all the possibilities of where traffic is coming from are quite complicated to assess.
Next, I erase the drawing and draw the junction again, but this time like this.
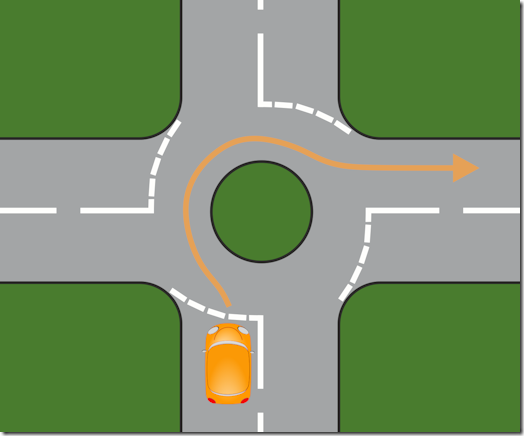 Again, I ask them to imagine they’re in the yellow car and want to turn right – so where do they need to look before they decide to go. We (eventually) settle with ‘to the right’ – though not always to start with. So now we end up with this.
Again, I ask them to imagine they’re in the yellow car and want to turn right – so where do they need to look before they decide to go. We (eventually) settle with ‘to the right’ – though not always to start with. So now we end up with this.
 At this point, I usually ask them why it is they can handle the crossroads situation, and yet they turn into a quivering blob of jelly the moment I say the word ‘roundabout’. The roundabout is actually far easier when it comes to the reasons they give for not liking them. All they have to do is learn to assess the red zone and that’s it – they can then just look where they’re going.
At this point, I usually ask them why it is they can handle the crossroads situation, and yet they turn into a quivering blob of jelly the moment I say the word ‘roundabout’. The roundabout is actually far easier when it comes to the reasons they give for not liking them. All they have to do is learn to assess the red zone and that’s it – they can then just look where they’re going.
Obviously, there’s a bit more, but this is a way of trying to demystify the whole roundabout situation.
Should I indicate to go straight ahead on a 3-exit roundabout?
Look at the mini-roundabout in this photo. The main road is A to B, and the side road leads off to a school and recreation area, and this is what it looks like as you approach it from A.
 Clearly, you do not signal left, because you are not going left into the school. But if you signalled right, what would the red car think you were going to do? If it was me driving the red car, I would think you were planning to turn right in front of me, so I’d stop.
Clearly, you do not signal left, because you are not going left into the school. But if you signalled right, what would the red car think you were going to do? If it was me driving the red car, I would think you were planning to turn right in front of me, so I’d stop.
This is the same roundabout, but this time approaching it from B. There is no car coming the other way in this picture, but if there was and you were not signalling, could the driver be certain you were not going to turn right into the school? Yet if you signalled left, you’d be giving a positive indication that you weren’t.
 If you came to the roundabout and no one was on the opposite side, a signal could be omitted. But if someone was approaching it, a left signal would help them.
If you came to the roundabout and no one was on the opposite side, a signal could be omitted. But if someone was approaching it, a left signal would help them.
See how this works? Each situation is different, but if you understand and think, it all becomes easier. If your signal helps someone and doesn’t confuse them then it is a good idea to use it. This is useful for most three-exit roundabouts.
Another useful exercise is to watch what other drivers do and ask yourself if they’ve helped or confused you by signalling or not signalling, and use that to develop your own strategy in future. Don’t be afraid or ashamed of changing the way you do things as you learn.
But you’re only supposed to signal if you’re changing direction, aren’t you?
No. This question arises from the idea that by going straight ahead on a roundabout you’re not “changing direction”. Driving: The Essential Skills (TES) – the official DSA guide – says:
Use signals
- to let others know what you intend to do
- to help other road users, including pedestrians
- in good time and for long enough to allow other road users to see the signal and act upon it
In the example I used in the previous question, if other road users can’t otherwise be sure of your intentions then using your indicators makes perfect sense. It is helping other road users.
Should I always indicate to go straight ahead?
NO!!! You still see older drivers indicating right when they’re going straight ahead and it is extremely confusing if you’re coming the opposite way. Apparently, this was taught once upon a time, and some people still use it. But it is wrong.
But you shouldn’t rely on people’s signals, should you?
No. And that’s because they often don’t signal or signal incorrectly. Giving a positive signal at the right time helps people. But other people getting it wrong doesn’t mean you should join them.
Isn’t this Highway Code roundabout diagram wrong?
No. This question arises periodically on social media from people trying to pick fault with the HC. Note how the green car turning right is shown exiting in the right hand lane – even though the arrows clearly show that it can exit in either the left or the right lane.
The diagram is absolutely correct, particularly in view of the fact that every entry road in the diagram has two marked lanes, implying that the roundabout itself has two lanes on it.
A good example of this is the Virgin Roundabout in Nottingham, which features on several Colwick test routes. An aerial view of it is shown here.
 The main road is a dual carriageway on one side, and two lanes quickly merging into one on the other (the yellow dotted lines). The two side roads are single lanes into industrial areas, one of which is sometimes used for test purposes (the green dotted line).
The main road is a dual carriageway on one side, and two lanes quickly merging into one on the other (the yellow dotted lines). The two side roads are single lanes into industrial areas, one of which is sometimes used for test purposes (the green dotted line).
The two lanes on the main road define the number of lanes on the roundabout, and this means that emerging from the industrial road in question requires careful thought.
It is perfectly acceptable to move across and merge with the left hand lane as you negotiate the roundabout as long as you do it safely. However, as I have already mentioned, learners are often unable to handle the extra safety aspects involved in switching lanes, especially on roundabouts. In this particular example, the main road is very busy and the likelihood of someone entering the roundabout in the left hand (yellow dotted) lane while you are on following the green dotted line is extremely high (it’s normal practice, in fact). For that reason, I explain clearly to all of my learners that the safest and easiest way to negotiate the roundabout is to remain in the right-hand lane and exit in that lane (as shown by the green line). Then, all they have to do is to allow others to merge from their left once they’re safely on the main road.
But ‘the 12 o’clock rule’ works!
No it doesn’t. Something only ‘works’ if it is never wrong and never leads to confusion for anyone. But it does lead to confusion for other drivers, and that is potentially dangerous.
Do you always position left for going straight ahead?
No, not always. In the simplest cases, yes. But it depends on the roundabout and the situation. This question came from a reader concerning a test route roundabout in Gloucester, shown here.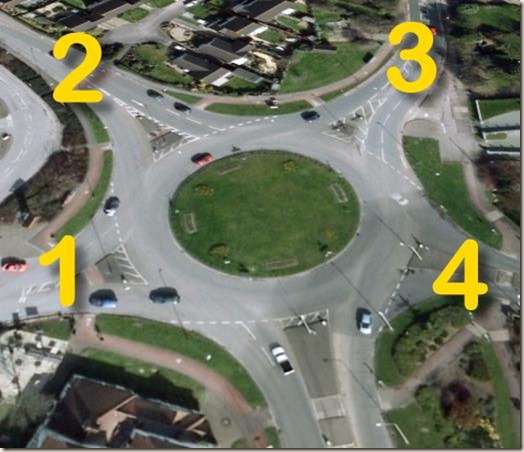
As you can see, it has five roads leading into it. The test route involves approaching from the road at the bottom and taking the third exit (3). The reader pointed out that the roundabout is completely unmarked and unsigned. So which lane should you use for the third exit?
Looking at the photo – and with the benefit of hindsight – I’d probably use the left hand lane position on approach for the exits 1 and 2, and the right hand lane position for the exits 3, 4, and 5. The reader points out that that’s what the examiners expect.
However, someone new to the area encountering that roundabout for the first time could easily attempt the third exit in the left hand approach lane. This clearly shows the importance of local knowledge, and further demonstrates why pupils really do need to be taught specific sections of test routes. There is no way most learners could handle features like this (there are no signs or road markings) if they encounter them for the first time on test.
Finally, I would not signal on approach for the 3rd exit. I can see how some might, and it probably wouldn’t matter so long as they cancelled and indicated left as the passed 2. If they cancelled late, it could be marked as a fault.
Do you always position right if you’re taking the 3rd exit or turning right?
No. Usually, you will, of course – but there are roundabouts where the left lane can have double- or even triple-headed arrows painted in it. However, if the roundabout is unmarked on approach or has no marked lanes then it is most likely you will use the default roundabout procedure and so adopt the right position if turning right – unless local knowledge says otherwise.
Which lane should I choose?
It depends. If the roundabout is a simple four-road one and is unmarked:
- for left or straight ahead you should approach in the left hand lane or position to the left if the approach is a single lane. You should stay in that lane until you have left the roundabout, remembering to signal at the exit before the one you want
- for right or full circle then you should approach in the right hand lane or position to the right, then check your mirror and signal at the exit before the one you want
If the roundabout is marked, or if it has more than four roads joining it (quoting the HC):
- choose the appropriate lane or position on approach
Signs or road markings might tell you what position to use. Sometimes, it is down to local knowledge and nothing else. Here’s an example submitted by a reader.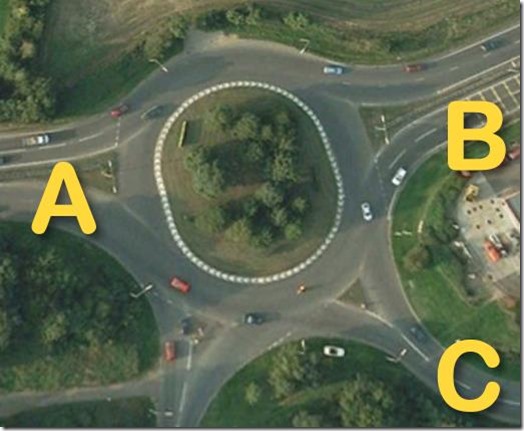
The A47 from Norwich (A) continues straight ahead to Great Yarmouth (B). It is a dual-carriageway on both sides. The second exit (C) goes to the village of Blofield. The reader asked which lane to use approaching from A when intending to exit via C.
Most marked roundabouts like this will have signs and road arrows telling you which lanes to use. Unless you really know what you are doing, if two or more lanes are going in your direction, stay in the one on the left as the safest option.
This particular example is complicated by the fact that the main feed roads are dual carriageways, and that changes the priorities somewhat. If you think about it logically, trying to negotiate from A to C in the left lane is potentially dangerous because – in the absence of road markings telling you otherwise – it is perfectly acceptable for people to travel A to B in either lane. That would mean that if you tried to go A to C in the left lane, colliding with someone in the right lane who was travelling A to B would be quite likely. This is yet another example of local knowledge being extremely valuable.
Can I fail for going straight ahead from the left lane?
Ordinarily, the left hand lane is the correct one for straight ahead. However, if the roundabout is non-symmetrical, has more than one ‘straight ahead’ (intermediate) exit, or if signs or road markings indicate otherwise, then the left lane may not be the correct lane to use.
There is no one-size-fits-all, unfortunately. Gaining local knowledge through a driving instructor is important in these sorts of cases. So yes, in some cases just defaulting left will result in a fail.
Why isn’t it the middle lane for going straight ahead?
Sometimes it is – if there is one. But it can just as often be another lane. The Nottingham Knight roundabout near me has three lanes on one approach, with the two left ones going left, and the right-hand one for straight ahead and right. In general, you should follow the underlying principle of ‘left lane for left or straight ahead… unless road signs or road markings indicate otherwise’.
What does ‘lane discipline’ mean?
It means choosing the correct lane, and/or staying in the correct lane, and/or doing the right checks before changing lanes. It applies to all aspects of driving, not just roundabouts. Many drivers haven’t got a clue how lanes work, and this is where their problems stem from.
Can I change lanes on the roundabout if I get into the wrong one?
Yes, as long as you have checked to make sure you aren’t going to interfere with anyone else. However, it is a risky operation unless it is very quiet, and if you are likely to impede someone just follow the lane you’re in and effectively ‘go the wrong way’. Then either find a place to turn around or simply carry on round the roundabout and select the correct lane the next time around.
On your driving test, being in the wrong lane is almost certainly going to be marked as a fault. If you cause someone to slow down by changing lanes or hesitating you’re probably going to get a serious or dangerous fault. If you don’t check properly before switching you’ll probably get a serious fault even if there’s no one there.
What do roundabout exit numbers mean?
This is just a way for you to know where you’re going when you are being given directions. I explained it at the beginning of this article.
Does a satnav tell you which lane to use?
No. Even if it did it would be dangerous to trust it. Roadworks, for example, can change how you use lanes and the satnav would not know that.
What about service roads?
The term ‘service road’ is a bit of a misnomer these days. The road in question is just as often a gateway to a retail park or other site where there is usually no through road. They can even refer to entrances to grit yards or private areas where you’re not allowed to drive anyway. They usually appear on signs as smaller roads like this.
The service road is that little dash at the 8 o’clock position. Sometimes, the dash is so small you could easily not see it as you drive past. I usually don’t include them in the exit count – so the 2nd exit here would still be the one just after the 12 o’clock position.
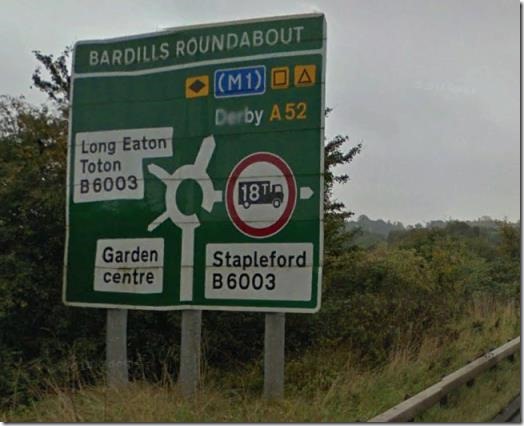 But they are all different. We have one in Nottingham on the A52 which looks like this on the sign.
But they are all different. We have one in Nottingham on the A52 which looks like this on the sign.
The garden centre is on a very small service road, and yet it has been designated as an actual roundabout exit by virtue of the length of the line.
Then you can have dual carriageways appearing as two dashes, like this (and I’ve included a service road).
Both carriageways are shown for each dual carriageway exit – but you only count each pair of dashes as a single exit. It is also common for dual carriageways to still only appear as a single dash on older signs.
It’s just a case of learning as you go along.
If the third exit is before 12 o’clock where do you position yourself in a roundabout?
As I have explained, there is no such thing as ‘the 12 o’clock rule. You simply use the same rules as for all the previous examples.
Remember that ‘straight ahead’ doesn’t automatically mean ‘the 2nd exit’. It depends on the road. Sometimes, ‘following the road’ can mean what would be virtually a right turn if you only looked at it from a geometric perspective.
If the 3rd exits is after 12 o’clock where do you position yourself in a roundabout?
As I have explained, there is no such thing as ‘the 12 o’clock rule’. You simply use the same rules as for all the previous examples.
Why do other people signal if it’s wrong?
You have to understand that simply having a driving licence does not automatically make someone a good driver. Some of them out there are appallingly bad.
As a result, you should never completely trust someone’s indicators – especially if they aren’t indicating at all.
What about these appendices to the Northern Ireland Highway Code?
A reader sent me a link, claiming that there is an appendix to the HC which advocates ‘the 12 o’clock rule’. The link is specifically for Northern Ireland (even though the reader is in England, and he should know that NI differs to the rest of the UK in several ways). The appendix in question is clearly not an official part of the HC, and it contradicts it directly. The actual NI HC says exactly the same thing as the UK one – except for this appendix.
What am I supposed to be checking for in my left mirror?
When you leave a roundabout, and especially when turning right, you need to make sure you’re not moving over into someone else’s path as you do.
What do I do if I’m leaving a roundabout and there is traffic on my nearside (left)?
Well, obviously you don’t want to end up colliding with the other traffic, so there’s your starting point. That leaves you with the choice of either slowing down slightly to give way to them, or continuing confidently and allowing them to give way to you. If there are two lanes, stay in yours and be careful.
Is it a ‘major’ if I stall at a roundabout?
It will be a driver fault if no one is there (or if you deal with it quickly or are lucky and the examiner is in a good mood). It will be a serious fault or worse if you cause a hold up of other danger. It is not automatically a serious/dangerous fault – but it can be.
What is ‘local knowledge’?
Precisely what it says – knowledge of how the locals deal with a situation. It doesn’t mean you can break the rules or anything, but it might be to do with how you position yourself to deal with a roundabout or other feature.
How do I enter a gridlocked roundabout?
There’s no simple answer to this. Every situation will be different. Above all else, you need to be both confident AND competent! Then it will come down to the realisation that unless you try to move out, you’re not going to get anywhere. Once you do start to edge out, someone will let you in.
What should I do if the traffic lights are out on a light-controlled roundabout?
In theory, treat it as a normal roundabout, giving way to traffic on your right. However, assume that everyone else on the road is an idiot who doesn’t understand this (trust me, it’s happened to me before, and everyone else IS an idiot in this scenario), and be very careful with traffic entering in front of you.
What is a spiral roundabout?
Personally, I don’t like this term and I don’t use it with my pupils (although I often explain it to them). All roundabouts are ‘spiral’ if you’re turning right – if you are on the inside nearest to the island, you’ve got to move out in order to exit.
The term is typically applied specifically to larger marked roundabouts – the ones that have a lot of lanes on them.
Why did I fail my test on roundabouts?
There is no specific mark for roundabouts on the DL25 marking sheet. Roundabout faults can come under a lot of things, usually related to lane discipline, observations, following road signs or road markings, correct signalling, planning, and so on.